En ligne depuis le 15/11/2022
0/5 (0)

Description
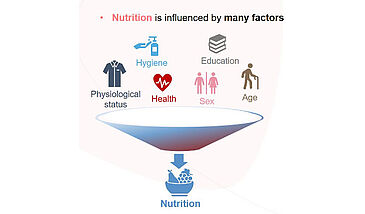
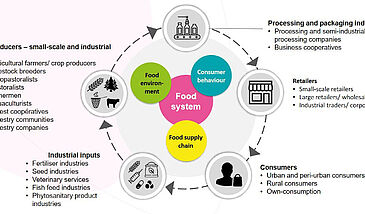
Over the last two centuries, technology has reduced the ever-present risk of starvation, enabling the world to feed itself despite exponential population growth. However, this achievement has come at a cost that renders the current food system unsustainable. We cannot rely on linear approaches to solve it, but rather, a systems approach is required.
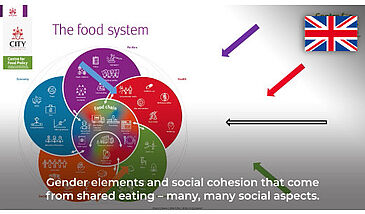
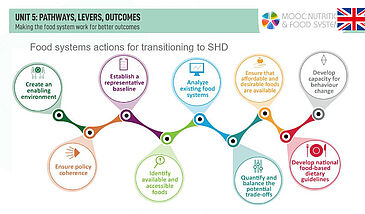
The food system can be described in terms of its component parts, its sustainability dimensions, its interactions with other systems, its drivers and outcomes, as well as in terms of its interactions between its component parts and feedback loops. Each part of the system affects the other parts, in a complex cycle of actions and reactions. Given this complexity, actions should be designed to optimize synergies and minimize negative consequences.
État
- Labellisé
Langues
- Anglais
- Langues étrangères
Licence Creative Commons
- Partage des conditions à l'identique
- Pas d'utilisation commerciale
- Pas de modification
Nature pédagogique
- Entretiens et témoignages
- Présentation
Niveau
- Bac+2
Objectifs de Développement Durable
- 2. Faim "Zéro"
Thèmes
- Alimentation
Types
- Vidéo (+ de 10 min)
Mots-clés
Liste de ressources
Contributeurs
Egal Florence
Senior Consultant at ONU-Habitat
Meybeck Alexandre
Senior Forests, Trees and Agroforestry Scientist at CIFOR
Fracassi Patrizia
Senior Nutrition and Food Systems Officer at FAO
Caron Patrick
chercheur , CIRAD - Centre de coopération Internationale en Recherche Agronomique pour le Développement
Hawkes Corinna
Director of the Center for Food Policy at City University of London
Aburto Nancy
Deputy Director of the Food and Nutrition Division , FAO
Bricas Nicolas
Chercheur au CIRAD & Directeur de la chaire UNESCO of World Food Systems , CIRAD - Centre de coopération Internationale en Recherche Agronomique pour le Développement
Raza Ahmed
Nutrition and Food Systems Officer , FAO